Fatigue is defined as a reduction in physical and/or mental capability as the result of physical, mental or emotional exertion which may impair nearly all physical abilities including: strength, speed, reaction time, coordination, decision making or balance.
Fatigue amongst seafarers is recognized as a serious issue affecting maritime safety. There is clear evidence that fatigue is a contributory cause of accidents such as injuries, death, long-term ill health, major damage to and loss of vessels and enormous environmental harm.
The IMO guidelines are composed of modules each devoted to an interested party. The modules are the following: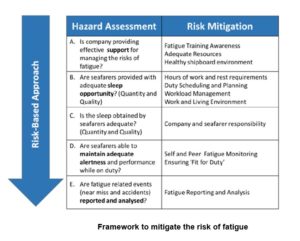
– Module 1 Fatigue
– Module 2 Fatigue and the company
– Module 3 Fatigue and the seafarer
– Module 4 Fatigue, awareness and training
– Module 5 Fatigue and ship design
– Module 6 Fatigue, the Administration and port State Authorities
– Appendix 1 Examples of sleep and fatigue monitoring tools
– Appendix 2 Example of a fatigue event report information
As per MSC.1/Circ1598, these guidelines should be taken into consideration when:
-developing, implementing and maintaining safety management systems under the ISM Code
-promoting fatigue mitigation and management
-promoting awareness of the causes and consequences of fatigue and developing and delivering training programmes and courses;
-conducting casualty or accident/incident investigations and
-preparing applications for minimum safe manning documents or when determining minimum safe manning levels for ships
Source: MSC.1/Circ1598
Contact us to conduct a detailed gap analysis &
to receive a professional advisory in your area of interest
